SWIFT CSP V2023
About
Empowering Banking Security with SWIFT CSP Excellence
In 2016, the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) established a Customer Security Programme (CSP) introducing the Customer Security Controls Framework (CSCF). The Program aims to drive transparency and improve the security posture across the global financial community. The SWIFT community consists of over 11,000 institutions worldwide – all of which are required to annually attest to the current CSCF.
What Can Elevate Do For Your Organization
With over a decade of experience in providing IT audits and compliance for our banking and financial clients, we understand the unique and ever-evolving challenges and threats financial service firms are under. Our team of security, privacy, and IT auditors specializes in providing our clients independent and valued control design, implementation, and operating effectiveness over your compliance framework. We work with you every step to ensure a successful attestation for CSP v2023.
SWIFT CSP Readiness
Your attestation readiness starts with proper planning. First, we meet with your team to understand your architectural type and the applicability of each control type to your operating environment. Our comprehensive review of your security posture is mapped directly to the CSCF v2023 requirements. Your compliance plan is based on your operating environment needs and is designed to achieve and maintain CSCF v2022 compliance.
SWIFT CSP Independent Assessment
Our approach to conducting an independent assessment is tailored between our proprietary SWIFT CSCF tool and the CSCF Independent Assessment Process Guidelines for all five SWIFT architecture types. Our SWIFT Process Steps are designed to ensure our assessments cover the requirements to verify the mandatory controls, without over-simplifying or over-complicating the process.
Remediation Plan
Working with your key business and security stakeholders, we review the remediation plan to ensure all gaps and recommendations are aligned to your operating environment and meet your compliance objectives. Elevate will provide an independent assessment that is aligned with your self-attestation report.
Ongoing Support
As your partner, we provide continued support to see you through your remediation plan, on-time and that the CSCF v2023 requirements are met. We offer our clients ongoing training and SWIFT updates and industry thought leadership to ensure your team remains informed as SWIFT continues to evolve its program.
Why is Compliance with SWIFT Important?
The SWIFT system manages almost every international money and security transfer in the world. The SWIFT system is a vast messaging network used by banks and other financial institutions to quickly, accurately, and securely send and receive money transfer-related information. The system processes over 46 million transactions per day through its network.
SWIFT is a member-owned cooperative that provides safe and secure financial transactions for its members. Their membership consists of more than 11,000 institutions in over 200 countries. Almost all forms of financial institutions from banks to security dealers, to asset management companies, etc., are in some way using one or more of SWIFT services.
As of 2023, SWIFT institutions are required to self-attest against the CSCF v2023, which comprises 3 overarching objectives, 7 principles, and a maximum of 32 controls, with comprehensive implementation guidelines by the architecture type. In addition, all institutions are required to perform an independent assessment to demonstrate their compliance with SWIFT CSCF v2023.

Who can perform an Independent Assessment?
Independent assessments are mandatory and can be conducted by:
- Internal (independent) Assessors: 2nd or 3rd lines of defense (compliance, risk management, or internal audit) anyone that does not report to the CISO.
- External Assessors: independent assessors or CSP assessment providers with cybersecurity assessment experience. External Assessors do not have to be selected from the SWFT directory of CSP assessment providers.
- Mixed Team: composed of internal and external assessors is also an option.
The requirement is for an assessment, not an audit, so ensure your independent assessor is not charging you excessive audit fees. Contact Us for a reasonable quote on an independent assessment fee or find us on the SWIFT directory of CSP assessment providers.*
*SWIFT does not certify, warrant, endorse or recommend any service provider listed in its directory and SWIFT customers are not required to use providers listed in the directory.
What are Factors for Compliance Complexity?
The current v2023 CSCF has up to 32 controls (24 mandatory and 8 advisories). The total number of controls and the components in scope is determined by the “SWIFT architecture type”, defined by how SWIFT members connect to the SWIFT network.
Each SWIFT member must determine which architecture type their infrastructure falls into. The breakdown for all five SWIFT Architecture types is below:
Architecture Type A1: The user owns the communication and messaging interface. Users that do not own a messaging interface but own their communication interface would still be considered this type.
Note: Users that own the license for the communication interface that is used on behalf of other users or operated for personal use by a third party outside the user environment are also included in Type A1.
Architecture Type A2: The user owns the messaging interface, but not the communication interface (the service provider owns the license).
Note: Users that own the messaging interface license that is operated on their behalf by a service provider or third party are also included in Type A2.
Architecture Type A3: The user uses a SWIFT connector for an application-to-application communication interface. This setup can also be used in combination with user-to-application communication. In such cases, controls pertaining to the GUI must also be implemented. This architecture type also includes hosted solutions of the SWIFT connector.
Architecture Type A4: The user uses a software application to connect via application-to-application with the connection hosted by a service provider. Users that previously identified as Architecture B or Architecture A3 will now be considered Architecture Type A4.
Architecture Type B: The user does not have any SWIFT-specific infrastructure. Two types of set-ups are considered for Type B: 1) Users access their messaging interface through a GUI application for a user-to-application connection. 2) Back-office applications communicate directly with service providers using APIs without connecting with a SWIFT messaging service for an application-to-application connection. Note: Users that only access SWIFT messaging services with a browser, exposed by Alliance Cloud or Alliance Lite2, are also included in T 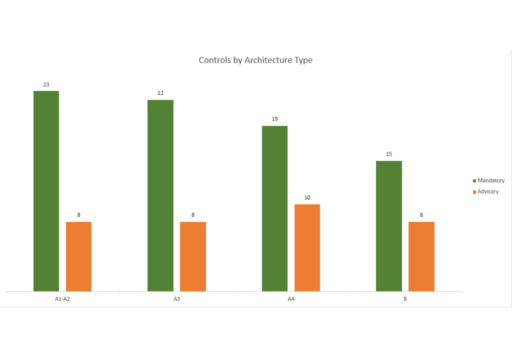
What is a Business Identifier Code (BIC)?
The general assumption is there is always one (and only one) BIC code that owns the license of the Messaging and Communication interface software. In the rare cases when there is no notion of BIC owner of the messaging Interface, SWIFT recommends that the user who owns (or the one operating) the communication interface self-attest as A1 while the other BIC codes attest as A2.
What Changed from 2022 to 2023?
- Control 2.2 (Security Updates) aligns the vulnerability remediation timeframes to common standard for security patching considering also the regular update deliveries
- Control 2.5A (External Transmission Data Protection) has been further clarified based on received queries
- Control 2.9 (Transaction Business Controls) clearly identifies the existing fifth element and asks, as optional enhancement, to combine several types of controls
- Control 4.2 (multi-Factor Authentication) also proposes to consider NIST SP 800-63B AAL2 for authentication factors selection/usage and remote-wipes in case of device theft/loss
- Control 6.1 (Malware Protection) specifically mentions, as optional enhancement, to consider all the general operator PCs, not only the Windows OS based on
- Control 6.5A (Intrusion Detection) focuses on the edge of the secure zone
- Control 7.3.A (Penetration Testing) identifies the multi-years essence of pentesting programmes that do not require to test everything at each exercise
